

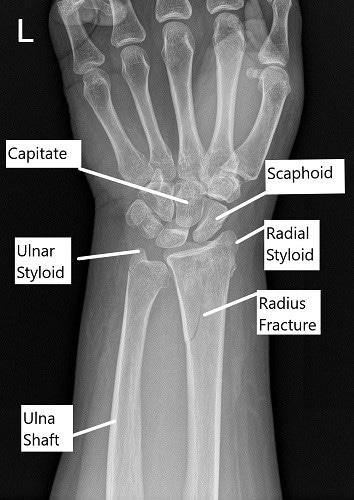
In cases where there is severe injury to the muscles, nerves or arteries, or there is significant contamination with dirt, rocks or grass from the injury, some patients require external fixation prior to definitive surgical treatment. Thus, patients have time to seek a second opinion regarding treatment if more information or additional surgeon input is desired. Ideally, surgeons like to perform surgery within 1-2 weeks of injury. Surgery takes under an hour and can often be done on a “same day” or outpatient basis. Pins use smaller incisions and are usually used for less serious injuries, or in kids with wrist fractures. Plates and screws require larger incisions, but ensure that the bone is lined up perfectly. Several studies have shown that surgery helps reduce pain, get people back to work sooner and maintains shoulder strength and motion.ĭistal radius fractures can be fixed with plates and screws or pins. Surgeons may recommend an operation to fix the broken wrist if it is broken into many pieces, if the bones are far apart, if the joint is uneven, if the bone sticks out through the skin, or if the nerves or blood vessels are injured. The cast is then removed, patients are given a removable wrist brace and physical therapy is started to help patients regain their range of motion. Wrist fractures treated non-operatively are usually casted for 6 weeks. If the bones lose their alignment or slip surgery may be required. Cutting down or quitting smoking and tight blood sugar control if you are a diabetic is important for the healing process. If non-operative care is chosen, regular follow-up care for a physical exam and x-rays is important to ensure that the fracture stays in good position and heals appropriately. Initially, splints are placed in the emergency room and converted to casts in the orthopedic office. Other displaced fractures can be “reduced” and casted, which means the doctor can push the bones back in place. Minor fractures with minimal displacement do very well with non-surgical treatment. Wrist fractures do not always require surgery, and many heal just fine without an operation. Non-Surgical Treatment for Wrist Fractures In cases where there are many pieces or severe intra articular fractures, a CT (Computed Tomography) Scan is ordered to help guide surgical treatment. Often three or more x-rays are taken to show the injury pattern. This helps doctors and patients make an informed decision on treatment. X-rays are used to evaluate the location, type, and severity of the broken bone.
#Wrist distal radius fracture skin#
Sometimes the bone pushes against the skin causing it to “tent.” Too much pressure can result in the bone coming through the skin. The doctor will also look for any open wounds over the injury. Sometimes patients with wrist fractures can develop acute carpal tunnel syndrome with numbness in the thumb, index and middle fingers. Important blood vessels and nerves lie near the distal radius, and can be injured when it breaks. Physical examination is important in the evaluation of these injuries. If this becomes uneven, wrist arthritis can occur. The distal radius does have a cartilage joint surface that helps the wrist joint glide smoothly.
#Wrist distal radius fracture full#
All the wrist bones are important for function and their shape and position must be perfect to allow for full wrist range of motion. The distal radius is the largest support bone of the wrist. Each requires specific types of treatment, so it is important for your doctor to diagnose and treat your injury appropriately. Other types of distal radius fractures include intra articular, extra-articular, simple and comminuted fractures. This is called an open fracture and needs urgent surgery. Sometimes the bone breaks and sticks out through the skin. The bone can break in many different ways and can range in severity. This can occur in patients of all ages from a variety of traumatic causes, and it is a very common injury. John Zebrack, MD General Orthopedic SurgeryĪ distal radius fracture is a break of the larger bone of the wrist. Jeffrey Webster, MD General Orthopedic Surgery Nichole Joslyn, MD Hand & Upper Extremity Thomas Christensen, MD Hand & Upper Extremity
James Christensen, MD Hand & Upper Extremity Nikola Babovic, MD Hand & Upper Extremity


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
